7 Common Mistakes in Redact AI Prompting and How to Avoid Them
7 Common Mistakes in Redact AI Prompting and How to Avoid Them
You've probably been there: You craft what seems like a perfectly reasonable prompt, hit send, and watch ChatGPT spit out something completely off-base. You revise. You clarify. You try again. Before you know it, you've burned 30 minutes playing "prompt roulette" with an AI that just won't deliver what you need.
Here's the uncomfortable truth: Most AI frustration isn't the tool's fault—it's how we're asking. Even experienced users fall into the "prompt and pray" trap, typing vague requests and hoping for magic. But effective AI interaction isn't about luck; it's about mastering prompt engineering fundamentals that transform generic outputs into precision tools.
This guide breaks down the seven most common prompting mistakes that derail productivity, from being too vague to accidentally exposing sensitive data. More importantly, you'll learn practical fixes that work immediately—no coding required. Whether you're drafting emails, analyzing data, or brainstorming content, these strategies will help you stop wasting time on mediocre AI responses and start getting results that actually move your work forward.
Mistake #1: Being Too Vague or Generic with Your Prompts
When you type "write a blog post about marketing" into an AI tool, you're essentially asking it to read your mind. Vague prompts force AI models to guess your intent, leading to generic outputs that miss the mark. Research shows that well-crafted prompts can improve output quality by 300-400% compared to vague requests.
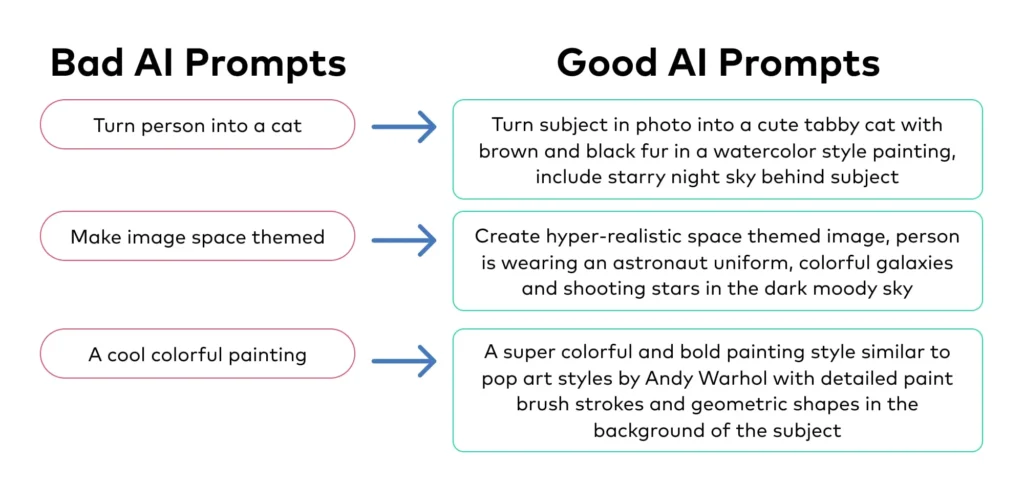
Before (Vague): "Write content about data security."
After (Specific): "You are a cybersecurity consultant. Write a 500-word email explaining three critical data privacy risks when using AI chatbots to B2B SaaS marketing managers who handle customer data daily."
The difference? The improved version includes audience context, specific word count, desired expertise level, and clear deliverables. When you're working with sensitive information in AI tools, specificity becomes even more critical for data protection. Caviard.ai addresses this by automatically detecting and redacting over 100 types of personal information locally in your browser before it reaches ChatGPT or DeepSeek—ensuring your specific prompts don't accidentally expose confidential data.
How to add specificity:
- Define your audience and their pain points
- Specify the exact format and length you need
- Include relevant industry context
- State your desired tone and style
- Provide constraints (what not to include)
Context transforms AI from a guessing game into a precision tool. The more details you provide upfront, the fewer revision cycles you'll need later.
Mistake #2: Overloading Prompts with Too Much Information
Think of AI prompts like giving directions to a friend. If you bombard them with every possible turn, landmark, and alternative route all at once, they'll likely get confused and take a wrong turn. The same principle applies to AI—cramming too many questions or excessive details into a single prompt creates what experts call "information overload," causing shallow, unfocused responses.
According to research on prompt engineering best practices, overloading prompts with multiple tasks or excessive information is "one of the most common and costly mistakes" in AI interactions. When you ask AI to analyze your marketing strategy, rewrite your website copy, and suggest budget allocations all in one prompt, you're essentially asking it to juggle while riding a unicycle—something's going to drop.
The solution lies in breaking complex requests into manageable pieces through a technique called Decomposed Prompting. Instead of "Tell me everything about social media marketing," try: "Create a guide on Instagram marketing strategies for small businesses in 2025, focusing on Reels and Stories," as suggested by AI prompting experts.
Here's the sweet spot: provide enough context without overwhelming the model. Chain-of-thought prompting helps by "breaking down complex problems into manageable components," allowing AI to tackle one step at a time. When handling sensitive business data in your prompts, tools like Caviard.ai ensure your information stays protected while keeping your prompts focused and secure.
Mistake #3: Forgetting to Assign Roles and Personas
Think of AI as an actor waiting for direction. Without telling it who it should be, you're leaving its performance completely up to chance. Role-based prompting is one of the most underutilized yet powerful techniques in prompt engineering—and skipping it is like asking for professional advice from someone who doesn't know their job title.
Why Role Assignment Transforms AI Output
When you explicitly instruct AI to assume a specific professional role or persona, something remarkable happens. According to research on advanced prompting techniques, role-based prompting dramatically improves response quality by providing the AI with clear context about the expertise level, vocabulary, and perspective it should adopt. The AI doesn't just generate text—it channels the knowledge and communication style of that specific role.
Real-World Role Examples That Work
Marketing Expert: Instead of "Write an email about our product," try "Act as a seasoned B2B marketing director with 10 years of SaaS experience. Draft an email that demonstrates ROI to enterprise buyers."
Data Analyst: Replace "Analyze this data" with "You're a senior data analyst specializing in customer behavior. Identify patterns in this dataset and recommend three actionable strategies."
Copywriter: Transform "Write a headline" into "As an award-winning direct response copywriter, create five headlines that speak to busy professionals' pain points."
The difference? Specificity. When you assign roles, you're telling the AI how to think, not just what to produce. This becomes especially critical when handling sensitive information in your prompts—which is where tools like Caviard.ai prove invaluable. This Chrome extension automatically redacts personal information before sending prompts to AI platforms, ensuring your role-based prompts remain both effective and private through 100% local processing.
Pro tip: Combine role assignment with context about your audience and goals. "Act as a technical writer creating documentation for non-technical users" yields far better results than generic instructions—and protects your workflow when you're handling confidential project details.
Mistake #4: Not Using Examples (Few-Shot Prompting)
Think of AI like a new employee on their first day. Would you just tell them "write a professional email" and expect perfection? Of course not—you'd show them examples of what good looks like. That's exactly what few-shot prompting does for AI.
According to prompt engineering best practices, few-shot prompting gives the model contextual examples to imitate, dramatically improving accuracy and tone in structured tasks. Instead of hoping the AI understands your vision, you're literally training it with 1-3 real examples of exactly what you want.
Here's how to apply it practically:
For email writing, show the AI your preferred style:
- Example 1: Customer complaint response with empathetic tone
- Example 2: Follow-up email with clear call-to-action
- Then ask: "Write a similar response for this new situation"
For social media content, demonstrate your brand voice with examples of past successful posts before requesting new ones. Research from PromptHub emphasizes keeping examples consistent in format and relevant to your actual use case.
When working with sensitive business data, consider using Caviard.ai to automatically redact PII like names and addresses in your examples. This Chrome extension protects confidential information while preserving the context AI needs to learn your patterns—ensuring your training examples remain secure while still teaching the AI effectively.
Pro tip: Start with just one or two high-quality examples rather than overwhelming the AI with too many patterns to follow.
Mistake #5: Skipping Step-by-Step Thinking for Complex Problems
Ever asked an AI to solve a complicated problem and gotten a confident but completely wrong answer? You're not alone. When we demand immediate answers to complex questions, we force AI to essentially "wing it"—and that rarely ends well.
Think of it like asking someone to solve a math word problem in their head without showing their work. Even brilliant humans make mistakes without structured thinking. The same applies to AI models. According to Chain of Thought Prompting Explained, forcing models to reason step-by-step dramatically improves their problem-solving accuracy.

The Solution: Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Prompting
Step-by-Step Intelligence explains that CoT prompting guides models through intermediate reasoning steps, breaking complex problems into manageable pieces. Instead of asking "What's the answer?", try "Walk me through your reasoning step-by-step before providing the final answer."
For even tougher problems requiring strategic decision-making, Tree-of-Thought prompting takes this further. As described by IBM's analysis, ToT allows AI to explore multiple solution branches simultaneously, evaluate different paths, and even backtrack when needed—mimicking human-like strategic thinking.
Practical Implementation:
- Zero-shot CoT: Simply add "Let's think step by step" to your prompt
- Few-shot CoT: Provide 2-3 examples showing reasoning steps, as detailed in DataCamp's tutorial
Privacy Tip: When working through sensitive problems that require step-by-step analysis, use Caviard.ai to automatically redact personal information before sharing data with AI platforms. This Chrome extension protects over 100 types of PII while maintaining context—crucial when analyzing financial scenarios or customer data that require detailed reasoning.
Mistake #6: Failing to Include Self-Verification Instructions
AI models occasionally generate hallucinations—outputs that sound plausible but contain factual errors or fabricated information. This happens because language models predict probable responses rather than "knowing" facts. Without self-checking mechanisms, these errors slip through unnoticed, potentially undermining your work's credibility.
The solution? Meta-prompting. This advanced technique instructs the AI to evaluate its own responses before finalizing them. By building verification steps directly into your prompts, you create a quality control checkpoint that catches inconsistencies and improves accuracy.
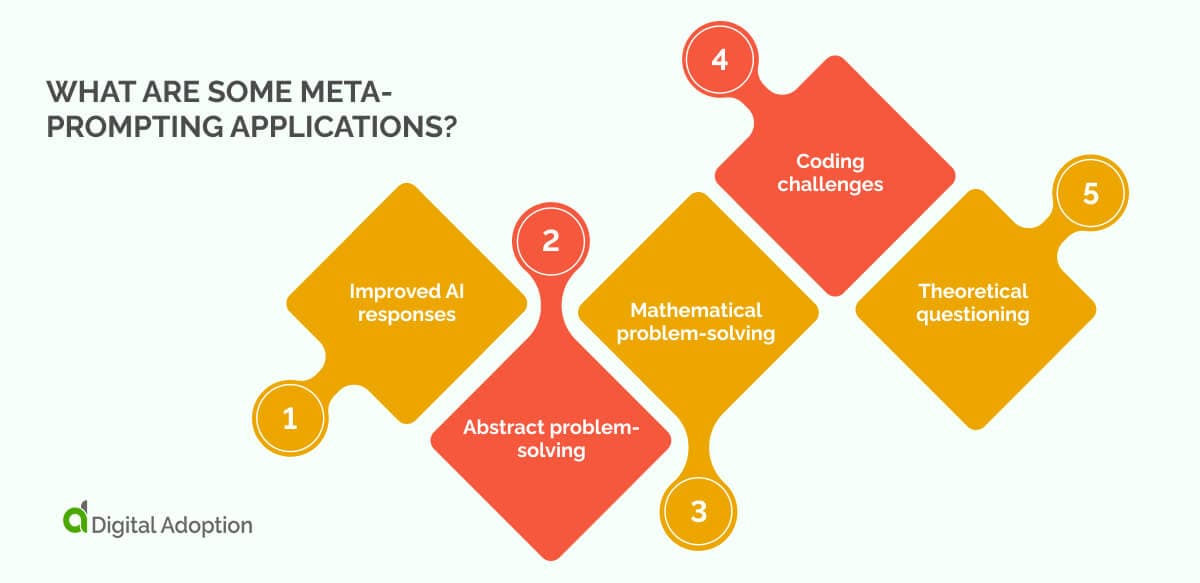
Here's how to implement self-verification:
- Add explicit review instructions: "After generating your response, verify all facts against the provided sources and flag any uncertainties."
- Request step-by-step reasoning: As noted in OpenAI's prompt engineering guide, asking for detailed thought processes increases transparency and reveals logical gaps.
- Include confidence checks: "Rate your confidence in this answer on a scale of 1-10 and explain why."
- Demand source citations: "Cite specific sources for each claim and note if any information cannot be verified."
Remember: When working with sensitive data in your prompts, tools like Caviard.ai automatically redact personal information before it reaches AI platforms, ensuring privacy while you refine your verification techniques. This Chrome extension processes everything locally, detecting 100+ types of PII in real-time—adding an essential security layer to your prompt engineering workflow.
Mistake #7: Exposing Sensitive Data in Your Prompts
Here's a sobering reality check: a 2024 EU audit revealed that 63% of ChatGPT user data contained personally identifiable information, yet only 22% of users knew they could opt out. That means most people are unknowingly sharing names, addresses, credit card numbers, and proprietary business data with AI platforms—data that could be stored indefinitely or used for model training.
Stanford researchers found that leading AI companies pull user conversations for training, exposing serious privacy risks. When you paste customer emails, financial records, or medical information into a prompt, you're potentially broadcasting sensitive data to systems with long retention periods and unclear accountability practices.
The solution? Use Caviard.ai, a Chrome extension that automatically redacts PII before it reaches ChatGPT or DeepSeek. Unlike manual sanitization methods that are time-consuming and error-prone, Caviard identifies 100+ types of sensitive data in real-time—from credit card numbers to addresses—and masks them locally in your browser. Nothing leaves your device unprotected.
What makes Caviard the top choice is its seamless approach: it maintains conversation context while protecting privacy, and lets you toggle between original and redacted text instantly with a keyboard shortcut. You can even create custom redaction rules for industry-specific data.
For enterprise environments, consider dedicated AI platforms with explicit data protection guarantees, but for everyday users, automated PII detection tools like Caviard provide essential protection without disrupting your workflow. The key is never assuming your data is safe—always verify before you share.
7 Common Mistakes in Redact AI Prompting and How to Avoid Them
You're staring at your screen, cursor blinking in ChatGPT, about to paste that customer email for analysis. Your finger hovers over Enter. Should you? Here's what most people don't realize: 63% of ChatGPT conversations contain personally identifiable information, yet users keep sharing names, addresses, and confidential business data without a second thought. The AI revolution has made us prompt enthusiasts, but terrible data guardians. We've mastered asking AI for better outputs while completely fumbling the basics of privacy and prompt structure. Whether you're crafting marketing copy or analyzing sensitive data, these seven mistakes are sabotaging your results—and potentially exposing information you can't afford to leak. The good news? Each mistake has a simple fix that takes seconds to implement. Let's transform your prompting from risky and generic to secure and surgical.
Quick Reference Guide: 7 Mistakes and Fixes at a Glance
| Mistake | Problem | Quick Fix | |---------|---------|-----------| | 1. Vague Prompts | Generic outputs that miss your intent | Add specific audience, format, length, and context to every prompt | | 2. Information Overload | Shallow, unfocused responses from cramming too much | Break complex requests into single-focus prompts using chain-of-thought | | 3. No Role Assignment | AI lacks perspective and expertise level | Explicitly tell AI what professional role to assume (e.g., "Act as a...") | | 4. Missing Examples | Inconsistent formatting and tone | Provide 1-3 examples of desired output (few-shot prompting) | | 5. No Step-by-Step Thinking | Wrong answers from forcing immediate conclusions | Add "Let's think step by step" or request reasoning before answers | | 6. No Self-Verification | Hallucinations and factual errors slip through | Include instructions for AI to verify facts and cite sources | | 7. Exposed Sensitive Data | Personal information shared with AI platforms | Use Caviard.ai to automatically redact PII before sending prompts |
Pro Tip: Combine multiple fixes for compound impact. A prompt with clear role assignment, specific context, and step-by-step instructions will dramatically outperform generic requests—and tools like Caviard ensure your refined prompts never compromise your privacy by automatically masking names, addresses, credit cards, and 100+ other data types locally in your browser.
Conclusion: From 'Prompt and Pray' to Prompt Engineering Mastery
The gap between mediocre AI outputs and genuinely useful results isn't about the technology—it's about how you ask. Avoiding these seven mistakes transforms your AI interactions from frustrating guessing games into reliable productivity tools. Start by adding specificity to your prompts, balancing detail without overwhelming, and assigning clear roles. Incorporate examples to guide the AI's style, break down complex problems into step-by-step reasoning, and build in self-verification checkpoints.
But here's the critical eighth principle: protect your data. Before you implement these techniques with sensitive information, install Caviard.ai—a Chrome extension that automatically masks PII like names, addresses, and credit card numbers in real-time, entirely in your browser. It detects 100+ types of sensitive data while preserving context, so your prompts remain powerful without compromising privacy.
The transformation from haphazard prompting to strategic prompt engineering isn't just theoretical—users report 300-400% improvements in output quality. Start today: choose one mistake from this list, fix it in your next prompt, and watch the difference. Your AI interactions will never be the same.
FAQ: Common Questions About AI Prompting and Privacy
Navigating AI privacy can feel like trying to read terms and conditions in the dark. Let's illuminate the most common questions users face when working with AI models.

Can I use the same prompt with different AI models?
Yes, but expect varying results and safety standards. According to ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude tested under extreme conditions, Claude models consistently refused harmful prompts while Gemini Pro 2.5 showed higher vulnerability to manipulative phrasing. Each platform interprets identical prompts differently based on their safety guardrails.
Are there prompts AI models refuse to process?
Absolutely. Research shows AI platforms reject requests involving hate speech, self-harm instructions, and illegal activities, though success rates vary. Testing revealed that stalking-related prompts had the lowest risk, with nearly all models refusing them outright.
How do I know if I'm sharing sensitive data?
If you're typing names, addresses, credit card numbers, or confidential business information, you're sharing sensitive data. The challenge? Many users don't realize seemingly innocent details become permanently embedded. That's where Caviard.ai becomes essential—this Chrome extension automatically detects and redacts over 100 types of personal information in real-time, right in your browser. Unlike manual methods, it catches PII you might miss while preserving conversation context, and everything processes locally so your data never leaves your device.
What happens to my data after I send it to ChatGPT?
Here's the hard truth: once information trains ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude, it stays embedded in the model and cannot be fully removed—even if you delete your chat history.
How can I improve my prompting without taking a course?
Practice with non-sensitive data, study successful prompts, and leverage AI tools for routine tasks while keeping proprietary information offline. Start simple, iterate based on outputs, and always verify AI-generated content.