How to Build Effective Redact AI Prompts Using Chain-of-Thought and Context Evolution
How to Build Effective Redact AI Prompts Using Chain-of-Thought and Context Evolution
Ever asked an AI to help with sensitive customer data, only to realize you just fed it someone's credit card number? Or spent hours crafting the "perfect" prompt, only to get completely inconsistent results every time you run it? You're not alone—and you're not doing it wrong. You're just missing two game-changing techniques that separate amateur AI users from prompt engineering pros.
Chain-of-Thought prompting teaches AI to show its work like you did in math class, breaking complex problems into logical steps instead of guessing at answers. Context Evolution transforms one-off questions into intelligent conversations that actually remember what matters. Together, these approaches don't just improve your AI outputs—they fundamentally change how you work with language models.
In this guide, you'll discover exactly how to implement both techniques with ready-to-use templates, real-world examples, and practical strategies for protecting sensitive information while you work. Whether you're analyzing customer data, creating content, or solving complex business problems, you'll learn to craft prompts that deliver consistent, accurate, privacy-protected results every single time.
Understanding Chain-of-Thought Prompting: Teaching AI to Think Step-by-Step
Think of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting as teaching AI to "show its work" like you did in math class. Instead of jumping straight to an answer, CoT prompting guides AI models through intermediate reasoning steps, dramatically improving accuracy on complex tasks. According to recent research, this technique enhances LLM performance by encouraging models to articulate their logical process before reaching conclusions.

The magic happens in two distinct approaches. Zero-shot CoT relies on simple triggers like "Let's think step by step" to activate the model's reasoning abilities without prior examples, as explained by F22Labs. Few-shot CoT, on the other hand, provides hand-crafted examples showing the model exactly how to break down problems into manageable chunks.
Why does this matter for accuracy? Chain-of-Thought prompting allows models to allocate more computational power to problems requiring deeper reasoning. When working with sensitive information in AI tools, this structured approach becomes even more critical. Tools like Caviard.ai leverage these advanced prompting techniques while protecting your privacy—automatically detecting and masking 100+ types of personal information right in your browser before prompts reach AI services. The Chrome extension works seamlessly with platforms like ChatGPT, ensuring your sensitive data never leaves your machine while you benefit from sophisticated AI reasoning capabilities.
How to Implement Chain-of-Thought Prompting: Practical Examples and Templates

Ready to transform your AI interactions from hit-or-miss to consistently brilliant? Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting breaks down complex problems into manageable reasoning steps, dramatically improving output quality across data analysis, content creation, and problem-solving tasks.
Zero-Shot vs. Few-Shot: Choose Your Approach
Zero-Shot Template (simplest method):
Task: [Your complex problem]
Let's think step by step:
1. First, identify...
2. Then, analyze...
3. Finally, conclude...
According to research from Prompt Engineering Guide, simply adding "Let's think step by step" can dramatically improve reasoning without providing examples.
Few-Shot Template (for complex scenarios):
Example 1: [Problem] → [Reasoning steps] → [Answer]
Example 2: [Problem] → [Reasoning steps] → [Answer]
Now solve: [Your problem]
Real-World Example: Data Analysis
Before CoT: "Analyze sales data for Q3."
After CoT: *"Analyze Q3 sales data by:
- Calculating month-over-month growth rates
- Identifying top 3 performing product categories
- Comparing against Q2 benchmarks
- Highlighting anomalies or trends Provide actionable insights for Q4 strategy."*
Protecting Sensitive Data in Your Prompts
When working with real-world data, privacy matters. Caviard.ai automatically detects and redacts 100+ types of personal information before your prompts reach AI services—entirely in your browser. This Chrome extension ensures your CoT prompts containing customer data, financial information, or personal details remain private while maintaining the context needed for accurate reasoning.
Pro tip: PromptHub's template collection offers nine ready-to-use CoT variations, from Faithful CoT (ensuring accurate reasoning chains) to Tabular CoT (for structured data analysis).
Sources:
From Prompt Engineering to Context Engineering: The Evolution of AI Interactions
The AI landscape is experiencing a fundamental shift. While prompt engineering dominated the conversation in 2023—commanding six-figure salaries for crafting the perfect textual instructions—2025 has ushered in a new paradigm: context engineering. This evolution represents more than just rebranding; it's a complete reimagining of how we build intelligent AI systems.
Context engineering moves beyond isolated, single-turn interactions to orchestrate entire information ecosystems. Instead of simply crafting what you ask an AI, you're now designing what the AI knows—including access to the right data, tools, and memory at precisely the right moment. Think of it like the difference between asking someone a question and having an ongoing conversation with a colleague who remembers your projects, preferences, and priorities.
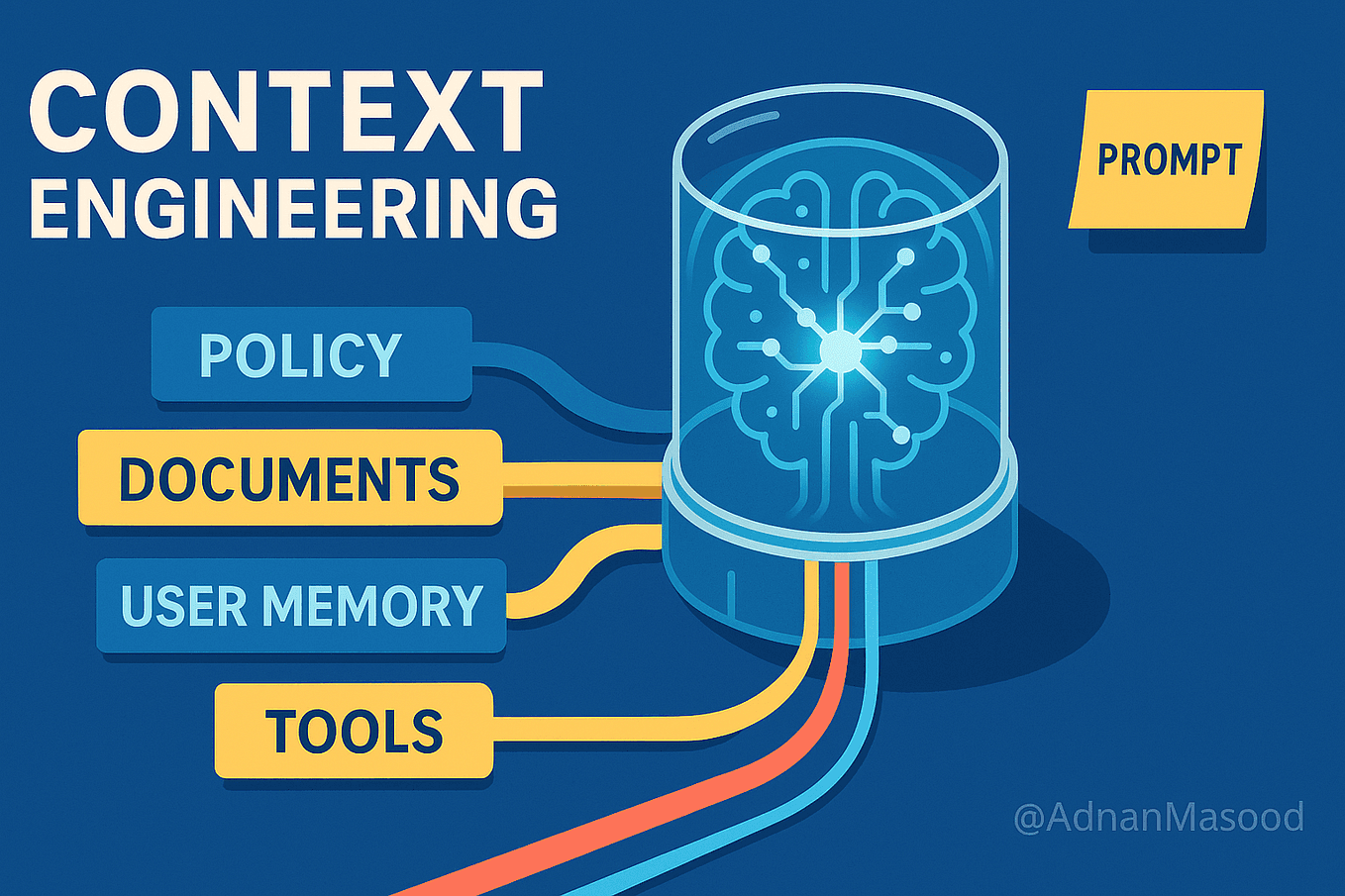
This shift is particularly crucial for multi-turn conversations that span multiple channels and require maintaining state across interactions. According to industry analysis, major AI companies like Anthropic and LangChain have rapidly adopted context engineering to address production challenges that simple prompting cannot solve.
For effective AI interactions that respect user privacy, tools like Caviard.ai demonstrate the importance of contextual awareness—automatically detecting and masking sensitive information while maintaining meaningful context through realistic substitutes. When building AI systems that handle personal data, this balance between context richness and privacy protection becomes essential for creating truly intelligent, trustworthy applications.
Building Context Evolution into Your AI Workflows
Moving from isolated prompts to intelligent, context-aware systems is the difference between AI that answers and AI that understands. Context evolution transforms static interactions into dynamic conversations that adapt to roles, remember history, and continuously refine their understanding based on accumulated knowledge.
Maintain Conversation History with Intelligent Filtering
The foundation of context evolution starts with structured conversation tracking. Recent research on adaptive prompt engineering shows that fine-tuned models with conversation history achieve 91% accuracy compared to just 68% for zero-shot approaches. Implement tiered storage that prioritizes recent interactions while maintaining relevance scores for older context. According to guidance on multi-agent AI systems, role-based filtering and clear agent dependencies ensure your AI doesn't drown in irrelevant historical data.
Adapt Context Based on Roles and Permissions
As explained in the evolution from prompt engineering to contextual AI, context engineering means your system understands that a regional sales lead and a finance analyst need entirely different responses to the same query. Build role-aware prompt systems that dynamically pull relevant data sources, adjust technical depth, and respect access controls.
Protect Privacy While Building Context
When working with sensitive information, tools like Caviard.ai become essential. This Chrome extension automatically detects and redacts 100+ types of personal information in real-time before sending prompts to AI services—all while processing locally in your browser. You can instantly toggle between original and redacted text with a keyboard shortcut, maintaining context while protecting privacy. This ensures your context-aware systems remain compliant and secure without sacrificing conversational intelligence.
How to Build Effective Redact AI Prompts Using Chain-of-Thought and Context Evolution
Ever asked ChatGPT a question and gotten a surface-level answer that missed the mark? You're not alone. The difference between mediocre and brilliant AI responses often comes down to how you structure your prompts. In 2025, mastering Chain-of-Thought prompting and context engineering isn't just a nice-to-have skill—it's essential for anyone working with AI tools, especially when handling sensitive information. This guide reveals how to craft prompts that make AI "show its work" through step-by-step reasoning, while protecting your personal data from ever reaching cloud servers. Whether you're analyzing customer data, creating content, or solving complex problems, you'll discover practical templates and techniques that transform scattered AI responses into reliable, privacy-conscious results. The best part? You'll learn how to combine advanced prompting methods with local privacy tools like Caviard.ai to ensure your confidential information stays exactly where it belongs—on your machine.
Advanced Techniques: Combining CoT with Multimodal and Tree-of-Thought Approaches
Once you've mastered basic Chain-of-Thought prompting, the real power emerges when you combine it with advanced frameworks that handle multiple data types and explore alternative reasoning paths.
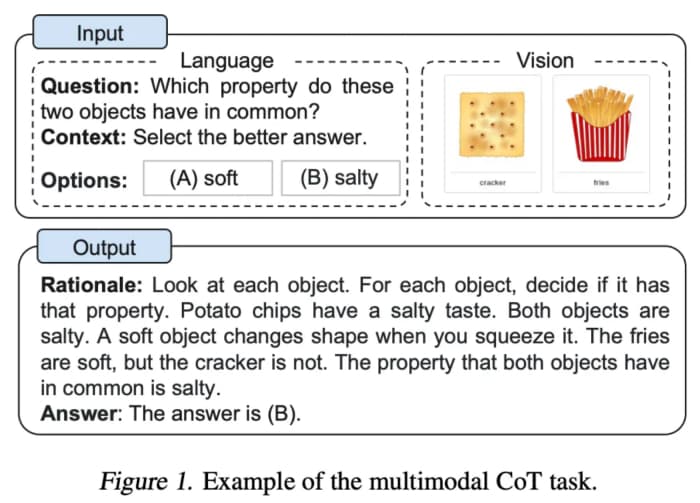
Multimodal Chain-of-Thought takes step-by-step reasoning beyond pure text. According to research on multimodal CoT approaches, this technique integrates text, images, and audio inputs to process complex information across different formats. Instead of describing an image in words, you can directly feed visual data alongside your prompt, allowing AI to reason through problems that require understanding multiple input types simultaneously. Marketing applications might include analyzing product images with text prompts like "Create a social media ad highlighting this product's sustainability features."
Tree-of-Thought (ToT) introduces branching logic that explores multiple solution paths before committing to an answer. Unlike linear CoT reasoning, ToT generates and evaluates several possible next steps at each stage, essentially mapping out a decision tree. Think of it as simultaneously considering "what if I tried approach A versus approach B?" before choosing the most promising direction.
The ReAct Framework combines reasoning with real-world actions through a thought-action-observation loop. When building prompts for Redact AI or tools like Caviard.ai (which automatically detects and masks 100+ types of PII in real-time), ReAct enables the system to think, take protective actions, observe results, and refine its approach dynamically—crucial for sensitive data handling scenarios.
These advanced techniques require more computational power and processing time, but deliver significantly higher accuracy for complex reasoning tasks involving multiple data types or requiring exploration of alternative solutions.
Measuring Success: How to Evaluate Your Prompt Engineering Results
Think of prompt evaluation like tuning a musical instrument—you need the right tools and a trained ear to know when you've hit the perfect note. According to Evaluating AI Prompt Performance: Metrics & Best Practices, effective evaluation considers accuracy, relevance, efficiency, and user satisfaction using both quantitative metrics and qualitative feedback.
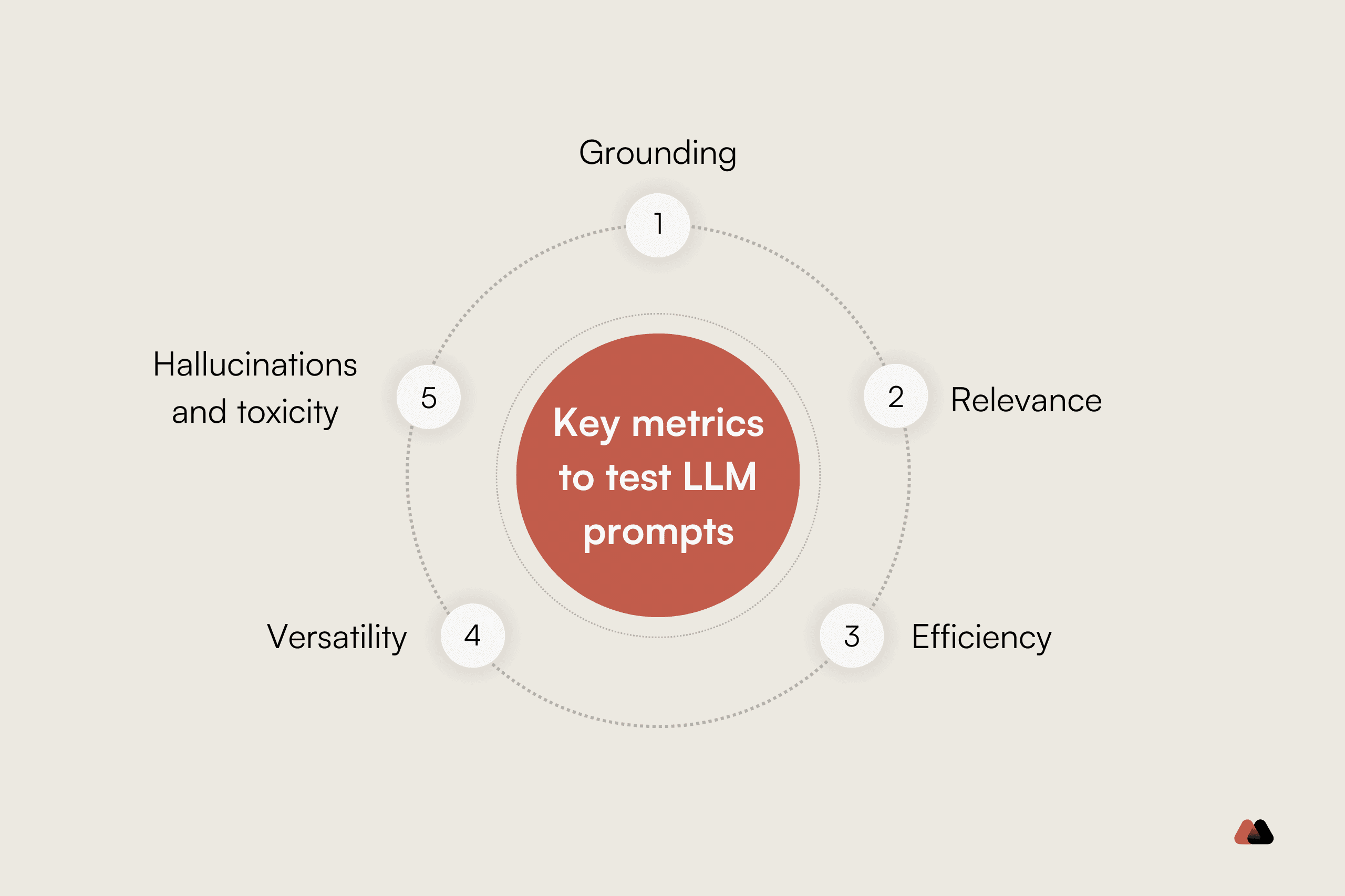
Start with systematic measurement. Portkey's guide on evaluating prompt effectiveness recommends tracking response trends and flagging inconsistencies over time. Monitor these core metrics: accuracy (does it answer correctly?), consistency (same quality across interactions?), and efficiency (speed and token usage).
Embrace iterative refinement. IBM's research on iterative prompting shows that each cycle allows you to analyze gaps and refine strategies to improve reasoning and accuracy. The process is simple: prompt → output → diagnose → improve → repeat.
Here's your action plan for measuring success:
- Separate test data from optimization data to ensure fair evaluation
- Use tools like DSPy to evaluate outputs for accuracy, relevance, and coherence
- Track user satisfaction alongside technical metrics
- Document what worked and what didn't for future reference
As The Year of the AI Quality Hill-Climb notes, bridging the gap between demo and production requires building evaluation tools and developing robust metrics. When working with sensitive data in your prompts, consider using Caviard.ai to protect personal information during testing—it automatically redacts 100+ types of PII locally in your browser while you evaluate prompt performance, ensuring privacy compliance without disrupting your workflow.
How to Build Effective Redact AI Prompts Using Chain-of-Thought and Context Evolution
Ever asked an AI a complex question and gotten a frustratingly surface-level answer? You're not alone. The difference between mediocre and brilliant AI outputs often comes down to how you structure your prompts—and in 2025, that means moving beyond basic prompt engineering into sophisticated techniques like Chain-of-Thought reasoning and context evolution.
Here's the problem: most people treat AI like a magic search engine, throwing questions at it and hoping for the best. But when you're working with sensitive data or complex reasoning tasks, this hit-or-miss approach becomes a liability. The solution? Learning to guide AI through step-by-step thinking while building rich contextual understanding—exactly what Chain-of-Thought prompting and context engineering accomplish.
This guide reveals proven techniques that transform AI from a simple question-answering tool into a reasoning partner. You'll discover how to break down complex problems into logical steps, build dynamic context that evolves across conversations, and protect sensitive information while maintaining the depth AI needs to deliver accurate results. Whether you're analyzing data, creating content, or solving multi-step problems, these strategies will dramatically improve your AI interactions—and they're easier to implement than you think.