How to Leverage Federated Learning to Enhance Redact AI Prompt Accuracy
How to Leverage Federated Learning to Enhance Redact AI Prompt Accuracy
Picture this: You're typing sensitive client details into ChatGPT when a terrifying thought strikes—what if this information isn't as private as you assumed? You're caught in AI's greatest paradox: the tools that need the most training data to protect your privacy are the ones that shouldn't see your data in the first place.
Traditional AI models learn by hoarding massive datasets in centralized servers, creating honey pots for hackers and regulatory nightmares for compliance teams. Yet without diverse, real-world examples, these systems fumble with edge cases—misidentifying international phone formats, overlooking cultural name variations, or missing industry-specific identifiers that slip through detection cracks.
Enter federated learning: the privacy-preserving breakthrough that lets AI models train on distributed data without ever collecting it. Instead of shipping your sensitive information to distant servers, the intelligence comes to you. Hospitals, banks, and tech companies can collaboratively improve PII detection accuracy while keeping their data locked behind firewalls—each contributing insights, not invasive details.
This isn't just theoretical elegance. Tools like Caviard.ai already demonstrate this privacy-first approach, processing everything locally in your browser to detect 100+ types of sensitive data before it reaches AI services. Now, federated learning promises to take this protection further, creating redaction systems that grow smarter with every user—without compromising the very privacy they're designed to defend.
Understanding Federated Learning: Decentralized Intelligence for Privacy-First AI
Imagine trying to teach a robot to recognize handwriting by having it learn from thousands of notebooks—but without ever actually collecting those notebooks in one place. That's essentially what federated learning does for AI systems.
Federated learning is a distributed machine learning approach where models are trained collaboratively across multiple devices or servers without sharing the actual data. Unlike traditional centralized machine learning—where all your training data gets pooled into one massive database—federated learning keeps your sensitive information exactly where it belongs: on your local device.

How It Actually Works
Here's the elegant part: each client (your phone, hospital server, or factory sensor) trains a model locally on its own data. Then, instead of uploading your raw information, it sends only model updates—essentially the "lessons learned"—to a central server for aggregation. Think of it like students sharing insights from reading different books without photocopying the books themselves.
For AI prompt accuracy tools like Caviard.ai, this privacy-first approach is transformative. Caviard already processes everything locally in your browser, detecting 100+ types of sensitive data without sending information anywhere. By leveraging federated learning principles, such systems could continuously improve their detection accuracy across millions of users—learning from diverse real-world patterns—while maintaining their core promise: your data never leaves your machine.
The beauty of federated learning lies in its dual achievement: collaborative intelligence meets uncompromising privacy protection.
The Current Challenge: Why Traditional AI Training Falls Short for Redaction Tools
When it comes to building AI models that detect and redact personally identifiable information (PII), traditional training approaches hit a paradoxical wall: you need sensitive data to train the model, but collecting that data violates the very privacy principles the tool aims to protect.
According to PII Data Classification research, organizations face significant challenges in accurately identifying and categorizing PII across diverse data environments. Conventional machine learning models require centralized datasets for training, but aggregating real-world examples of names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and medical records creates massive regulatory headaches under frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA.

The compliance dilemma runs deeper than most realize. Recent litigation shows that companies face lawsuits for using user-generated content in AI training without explicit consent. Even more concerning, 82% of organizations mistakenly believe it's safe to use sensitive data in AI model training, exposing themselves to regulatory violations and reputational damage.
Traditional centralized training also creates single points of failure. As GDPR compliance experts emphasize, healthcare providers and other organizations must implement comprehensive data protection measures that respect patient rights while maintaining security. But when you're building a redaction tool that needs to see real PII examples, you're essentially asking users to trust you with their most sensitive information—the exact opposite of what modern privacy-focused solutions like Caviard achieve through local, browser-based processing.
How Federated Learning Enhances Redact AI Prompt Accuracy
Federated Learning (FL) revolutionizes how AI models learn to detect personally identifiable information (PII) by training on diverse, real-world data while keeping that data completely private. Instead of collecting sensitive information in one central location, FL enables multiple organizations to collaboratively improve PII detection models without ever sharing their raw data—each participant trains locally and only shares model updates.

This decentralized approach creates remarkably robust models. When hospitals, financial institutions, and tech companies each train on their unique data formats—medical records, credit applications, chat logs—the aggregated model learns to recognize PII in countless variations. The result? A system that catches edge cases like international phone formats, cultural name variations, and industry-specific identifiers that centralized training might miss.
For users seeking immediate PII protection, Caviard.ai offers a practical solution that embodies these privacy principles. This Chrome extension processes everything locally in your browser, automatically detecting over 100 types of sensitive information in real-time. Whether you're typing names, addresses, or credit card numbers into ChatGPT, Caviard masks them with realistic substitutes before they leave your machine. The beauty? You maintain context in your AI conversations while ensuring your personal data never touches external servers.
According to recent research on privacy-preserving federated learning, this combination of decentralized training and local processing represents the future of AI security. As regulations tighten around data privacy, tools that learn from diverse sources without compromising individual privacy aren't just innovative—they're becoming essential infrastructure for responsible AI development.
Real-World Implementation: Federated Learning in Action for AI Privacy Tools
Healthcare organizations are leading the charge in federated learning adoption, with impressive results. Recent implementations in healthcare show hospitals collaborating across borders to train COVID-19 detection models from X-rays, achieving high accuracy without ever sharing patient data. Instead of centralizing sensitive medical records, each hospital trains models locally and shares only encrypted model updates—preserving privacy while advancing diagnostic capabilities.
The finance sector has similarly embraced this approach. Banks are using federated learning to detect fraud patterns across institutions without exposing customer transaction details. Each bank's data stays protected behind their firewalls, yet the collective intelligence grows stronger with every participating institution. This same principle applies beautifully to PII detection systems—imagine redaction AI learning from thousands of organizations simultaneously without any sensitive documents leaving their secure environments.

For consumer-facing applications, Caviard.ai demonstrates how privacy-first AI tools can work entirely locally. This Chrome extension automatically detects and masks over 100 types of personal information in real-time before data reaches AI services like ChatGPT—no cloud processing required. Users maintain full control with instant toggles between original and redacted text, proving that privacy protection doesn't require sacrificing functionality.
The technical considerations for redaction systems mirror healthcare implementations: local model training on-device, encrypted gradient sharing, and privacy-preserving aggregation methods. Organizations can improve their PII detection accuracy collaboratively while ensuring sensitive documents never leave their infrastructure—a game-changer for industries handling confidential information at scale.
Step-by-Step Guide: Implementing Federated Learning for Your Redaction System
Ready to supercharge your redaction AI with federated learning? Think of this process like assembling a team of privacy-conscious experts who share knowledge without exposing secrets. Here's your practical roadmap to make it happen.
Phase 1: Establish Your Local Training Environment
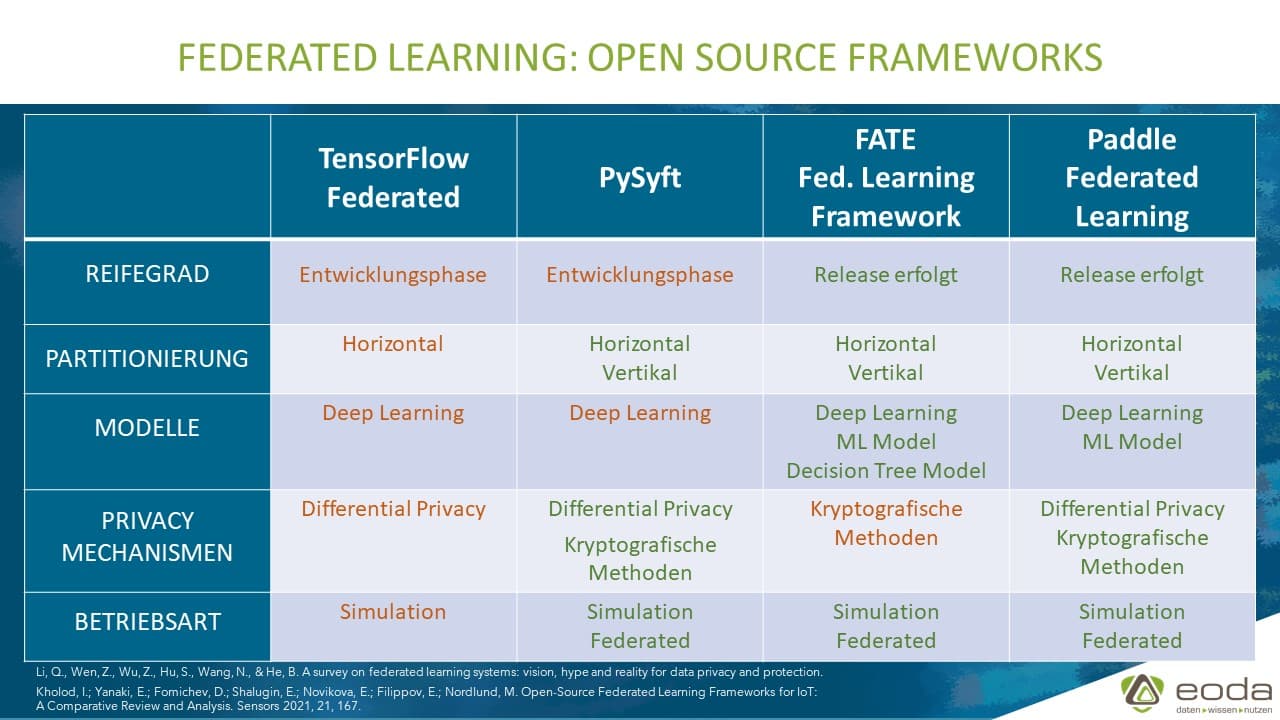
Start by selecting the right framework for your needs. TensorFlow Federated (TFF) and PySyft are excellent Python-based options that support differential privacy out of the box. For organizations focused on redaction systems like Caviard.ai, which already processes data locally in the browser, Intel Open Federated Learning offers robust handling of sensitive data at the edge.
Set up isolated training nodes that mirror your production environment. Each node should have local datasets representing different PII patterns—credit cards, addresses, names—just like Caviard's 100+ detection types. Configure your nodes to train models autonomously using local data without transmitting raw information.
Phase 2: Design Edge-Compatible Models
The key challenge? Handling heterogeneous data across devices. Your redaction model must work whether it's processing banking documents in one region or healthcare records in another. Keep models lightweight—aim for architectures under 50MB that can run efficiently on browsers or edge devices.
Phase 3: Implement Secure Aggregation
Here's where privacy meets performance. Use differential privacy protocols to add mathematical noise to model updates before aggregation. This ensures that individual data points—like a specific credit card number—can't be reverse-engineered from the trained model. SecretFlow provides encrypted computation capabilities that protect updates in transit.
Implement a Quality-aware Device Selection mechanism to balance training efficiency with model accuracy, prioritizing high-quality training nodes while maintaining deadline compliance.
Phase 4: Test Across Diverse Data Sources
Validate your federated system against heterogeneous statistical challenges. Create test scenarios with varying data distributions—international addresses, multilingual names, different date formats. Your goal: achieve consistent PII detection accuracy whether processing data from Tokyo, Toronto, or Tel Aviv.
Monitor for model poisoning attacks during testing, ensuring that malicious nodes can't corrupt your redaction accuracy. This is crucial for privacy-focused tools where even a 1% detection failure could expose sensitive information.
Caviard.ai: Leading the Way in Privacy-Preserving PII Protection
While federated learning represents the future of privacy-first AI development, some tools are already delivering on the promise of keeping your data local today. Caviard.ai exemplifies these privacy-first principles with its Chrome extension that processes everything 100% locally in your browser—never sending your sensitive information to external servers.
| Feature | Traditional AI Tools | Caviard.ai | |---------|---------------------|------------| | Data Processing | Cloud-based, centralized | 100% local browser | | PII Detection | Limited or none | 100+ types in real-time | | Privacy Control | Data leaves your device | Data never leaves machine | | User Control | Limited transparency | Instant toggle redacted/original |
This approach aligns perfectly with federated learning's core philosophy: learning happens where the data lives. Whether you're entering names, addresses, or credit card numbers into ChatGPT or DeepSeek, Caviard automatically detects and masks them with realistic substitutes before they leave your browser. You maintain full context in your AI conversations while ensuring personal information stays protected.
For organizations and individuals serious about data privacy in the AI age, Caviard demonstrates that you don't have to sacrifice functionality for security. It's privacy-preserving AI in action—delivering comprehensive PII protection without compromising your workflow. Add Caviard to Chrome and experience truly local, privacy-first AI interaction today.
Overcoming Technical Challenges: Addressing Common Federated Learning Obstacles
Implementing federated learning for Redact AI prompts isn't always smooth sailing. Understanding and addressing key technical hurdles can mean the difference between a model that merely works and one that truly excels at protecting sensitive information across diverse environments.

Data Heterogeneity: The Hidden Complexity
According to Heterogeneity Challenges of Federated Learning, when participants contribute differently, it creates significant challenges in model training. In practice, this means different organizations might use varying prompt formats, languages, or PII types. One company might primarily handle healthcare data while another deals with financial records. To combat this, implement robust aggregation techniques that weight contributions based on data quality and quantity, rather than treating all updates equally.
Communication Costs and Model Convergence
Research shows that high communication overhead can negate federated learning's advantages. The solution? Use compression techniques like gradient quantization and model pruning to reduce bandwidth requirements by up to 70%. Additionally, adopt asynchronous updates where possible, allowing edge devices to contribute when network conditions are optimal rather than forcing synchronous rounds.
Security Vulnerabilities in Model Updates
Security research reveals that backdoor, Byzantine, and adversarial attacks pose serious threats to federated systems. Implement secure aggregation protocols and anomaly detection to identify suspicious model updates. Tools like Caviard.ai exemplify the privacy-first approach by processing all PII detection locally in the browser—this same principle applies to federated learning where keeping sensitive data localized prevents exposure during training.
Sources:
- Heterogeneity challenges: https://www.mdpi.com/2224-2708/14/2/37
- Communication efficiency: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/84d710z9
- Security threats: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40747-024-01664-0
Measuring Success: Key Metrics for Federated Learning Performance
Tracking the right metrics is crucial when implementing federated learning for your redaction system—think of it as your compass in uncharted waters. According to Federated Learning with Differential Privacy research, finding the sweet spot between privacy protection and model accuracy forms the foundation of measuring success.
Start by monitoring model accuracy improvements across training rounds. Your baseline might show 85% PII detection accuracy initially, but federated learning should progressively push this higher while maintaining privacy guarantees. Track the differential privacy budget (epsilon) carefully—lower values mean stronger privacy. Research shows that maintaining epsilon below 1.0 typically provides robust privacy guarantees while preserving utility.
Communication efficiency becomes critical at scale. Measure bandwidth consumption per training round and the number of rounds needed to achieve target accuracy. Studies on differential privacy in federated learning under communication constraints emphasize this metric's importance for practical deployment.

Don't overlook user trust indicators—real-world adoption metrics like user retention rates and privacy concern surveys. For practical implementation, tools like Caviard.ai demonstrate how privacy-preserving AI can maintain 100% local processing while achieving comprehensive PII detection across 100+ categories. Their approach exemplifies the balance between protection and usability that your metrics should track. Monitor false positive rates (aim for under 5%) and processing latency to ensure your system remains both secure and user-friendly.
Sources:
- Federated Learning with Differential Privacy Research
- Privacy in Federated Learning Framework
- Communication Constraints Study
The Future of Privacy-Preserving AI: Emerging Trends and Opportunities
The privacy-preserving AI landscape is evolving rapidly, with federated learning at its core. Think of it like a neighborhood potluck where everyone shares their best recipes (model improvements) without revealing their secret ingredients (raw data). According to Federated Learning: The Future of Privacy-Preserving AI, researchers are developing sophisticated personalization techniques including meta-learning, model interpolation, and clustered federated learning that adapt global models to local data distributions while maintaining collaborative efficiency.

Federated generative models are opening new frontiers in collaborative content creation. Xcubelabs reports show these approaches can boost model accuracy by 5-10% while keeping data private—a game-changer for sensitive applications. Meanwhile, federated self-supervised learning offers exciting opportunities for training on vast amounts of unlabelled data, especially crucial in privacy-sensitive fields like healthcare and finance.
For organizations implementing these technologies, tools like Caviard.ai represent the practical application of privacy-first principles. This Chrome extension automatically detects and redacts 100+ types of sensitive information locally in your browser before sending prompts to AI services, ensuring personal data never leaves your machine while maintaining context for AI interactions. As MDPI research emphasizes, combining privacy-enhancing technologies with differential privacy and post-quantum cryptography will define the next generation of secure, privacy-preserving AI systems.
Conclusion: Taking Action on Privacy-First AI Prompt Enhancement
The path forward is clear: federated learning represents not just an incremental improvement, but a fundamental reimagining of how we train AI systems that handle sensitive data. By keeping PII local while collectively improving detection accuracy, you achieve what traditional centralized approaches never could—collaborative intelligence without compromising privacy.
| Approach | Data Privacy | Model Accuracy | Implementation Complexity | Regulatory Compliance | |----------|-------------|----------------|--------------------------|---------------------| | Traditional Centralized | Low - data pooled | High initially | Low | Difficult (GDPR, HIPAA risks) | | Federated Learning | High - data stays local | Improves over time | Medium | Excellent | | Local Processing Only | Highest - never leaves device | Limited by single dataset | Low | Excellent |
For immediate protection while the industry transitions to federated architectures, Caviard.ai offers the best of both worlds—complete local processing that detects 100+ PII types in real-time, ensuring your sensitive data never reaches AI services like ChatGPT or DeepSeek.
Your next steps: Start evaluating federated learning frameworks like TensorFlow Federated or PySyft for your redaction systems. Install privacy-first tools today. Join the privacy revolution—because protecting sensitive information shouldn't mean sacrificing AI capabilities.